Updated 25 November 2025 at 14:02 IST
2025 Ozone Hole Fifth Smallest Since 1992, On Track To Recover
The ozone hole over the Antarctic is significantly smaller in 2025 than in previous years, ranking as the fifth-smallest since 1992, according reports. NOAA and NASA scientists emphasize that the recent findings show efforts to limit ozone-depleting chemical compounds are having a significant impact
- Science News
- 2 min read
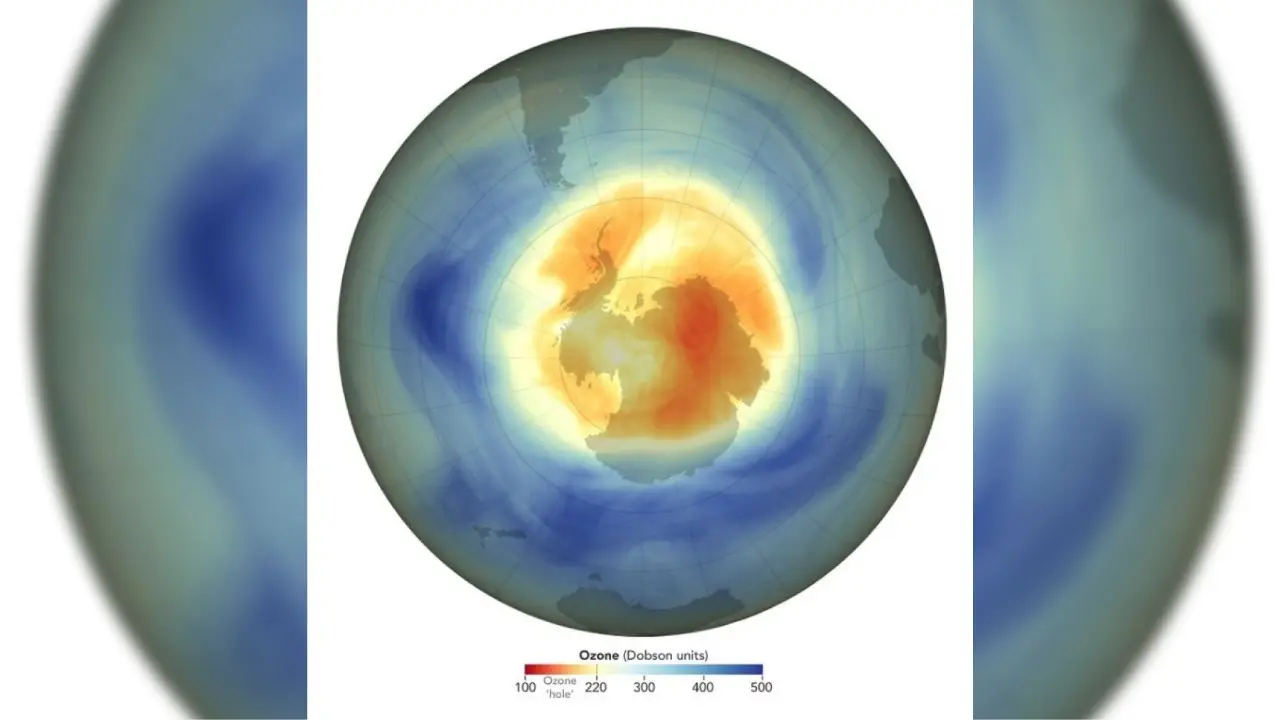
The ozone hole over the Antarctic is significantly smaller in 2025 than in previous years, ranking as the fifth-smallest since 1992, according to a new report by NOAA and NASA scientists.
The ozone hole reached its greatest one-day extent in 2025 in early September, measuring 8.83 million square miles—about 30% smaller than the largest hole on record in 2006.
The so-called “ozone hole” is not an actual hole in the planet’s ozone layer, but rather a large region of Earth’s stratosphere with extremely low ozone concentrations.
NOAA and NASA scientists emphasize that the recent findings show efforts to limit ozone-depleting chemical compounds are having a significant impact.
Advertisement
The regulations are established by the Montreal Protocol, which went into effect in 1992. Subsequent amendments are driving the gradual recovery of the ozone layer, which remains on track to fully recover later this century as countries worldwide replace harmful substances with safer alternatives.
“This year’s hole would have been more than one million square miles larger if there was still as much chlorine in the stratosphere as there was 25 years ago,” said Paul Newman, a senior scientist at the University of Maryland system and longtime leader of NASA’s ozone research team.
Advertisement
For decades, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other ozone-depleting compounds were widely used in aerosol sprays, foams, air conditioners, and refrigerators, causing significant reductions in ozone levels.
Natural factors, such as temperature and atmospheric circulation, also influence ozone concentrations and are likely to have contributed to a smaller ozone hole this year, according to researchers.
Earth’s ozone layer acts as a planetary sunscreen, shielding humans, animals and plants from harmful ultraviolet radiation. When ozone levels drop, more UV rays reach the surface, increasing the risk of adverse health and environmental impacts such as crop damage, skin cancer, and cataracts.
Published By : Ankita Paul
Published On: 25 November 2025 at 14:02 IST
